
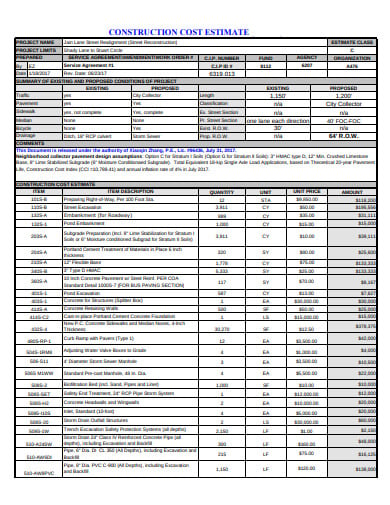
Next, you will check how accurate they are. You have created a 3D building footprints layer with roof form information in the attributes. Now that you have the buildings created, you will check how closely they match the lidar data. For now, you don't need to worry about it. This field is used for manually editing roof forms that were incorrectly extracted.
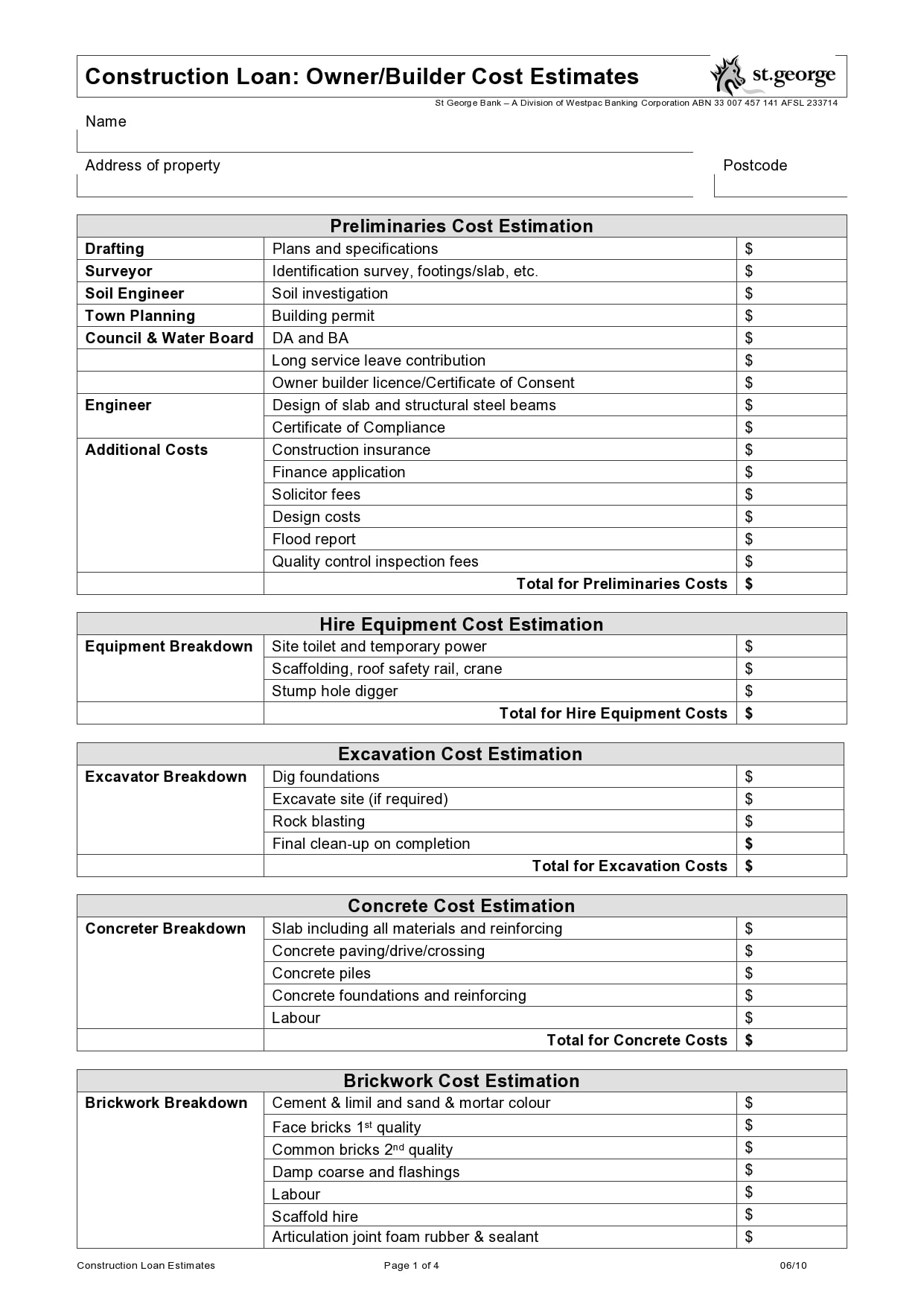
A value of 1 will rotate the roof counterclockwise 90 degrees, while a value of 2 will rotate it 180 degrees.
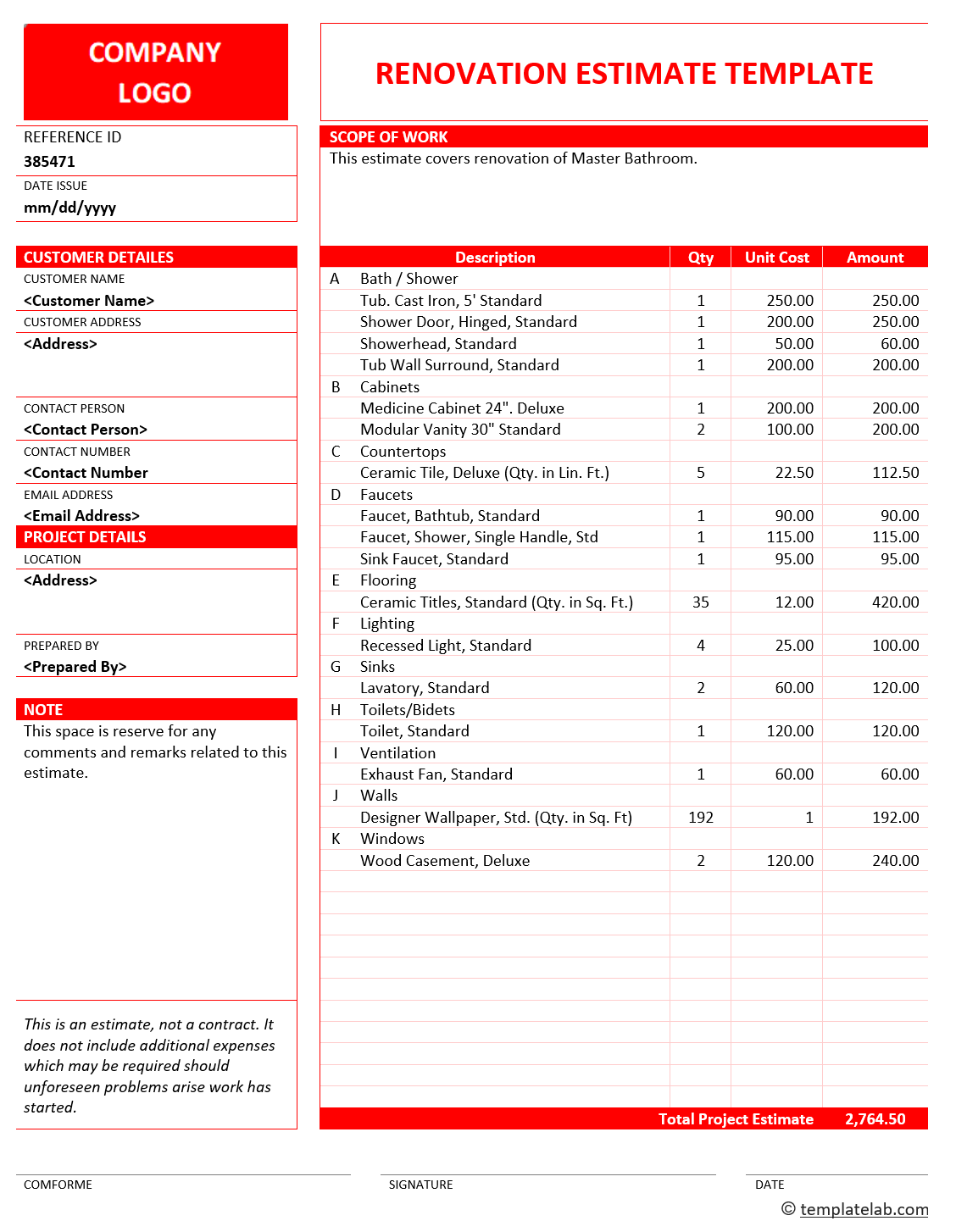
BASEELEV (Base Elevation)-The base height of the building, usually equal to the ground elevation where the building is located.The following image shows what each roof form looks like: The roof form can be Flat, Gable, or Hip. ROOFFORM (Roof Form)-The shape of the roof.Buildings with no eave height have flat roofs. EAVEHEIGHT (Eave Height)-The minimum height of the building.BLDGHEIGHT (Building Height)-The maximum height of the building.The fields and their meanings are explained in the following list: These fields were created by the Extract Roof Form tool based on the elevation layers and building footprints used as the tool's input. Alongside standard feature class attributes such as OBJECTID, Shape, Shape_Length, and Shape_Area, there are several fields related to roof height, form, and direction. These attributes will then be used to procedurally create these features in 3D. The Extract Roof Form tool will not automatically create 3D buildings, but it will add attribute data to 2D building footprints that describe roof form and other roof attributes. To extract roof forms, you will use the Extract Roof Form tool, which is one of the two script tools included in the Roof_Form_Extraction toolbox that you downloaded with the project data. Finally, you will check the features for potential errors. You will then use those attributes to symbolize the building footprints as 3D features. In this lesson, you will use these elevation layers and the building footprints to calculate attribute data for roof forms and heights. In the previous lesson, you converted lidar data into three elevation layers: one showing elevation of the ground (DTM), one showing elevation of features and buildings on top of the ground (DSM), and one showing height of features above ground (nDSM). Turn off all layers except Portland_dtm_surface and the basemap.Because the DTM shows the ground elevation and the DSM shows the elevation of the features on top of the ground (the absolute elevation), an nDSM shows the height of features above ground (the normalized elevation) to accurately process areas where roofs are expected to be. Unlike the DTM and DSM elevation layers, which were made from the LAS dataset, the nDSM is made by subtracting the values in the DTM from the values in the DSM. The locations of buildings still show up faintly because the tool estimates the location of the ground based on surrounding points. Darker areas have lower elevations, and lighter areas have higher elevations. The DSM shows the elevations of buildings and other features. You have now created the three elevation layers you will use when you run the Extract Roof Forms tool. Most of the ground area has a value of 0 or close to 0 (the black cells). The nDSM shows the relative height of the structures.
Online building estimate form pro#
You will also open an ArcGIS Pro task to take you through the workflow step by step.
Online building estimate form download#
Download the data and deploy the solutionīefore you begin, you must download data supplied by the City of Portland and deploy the ArcGIS Solutions 3D Basemaps. The links change frequently, so just search for ArcGIS Solutions in any web browser. You can visit the ArcGIS Solutions page for more information. Then, you will convert the point cloud into raster datasets that show the elevation of the area. After downloading the project and data, you will convert raw lidar data of the Portland neighborhood into a 3D point cloud (LAS) dataset that shows where light from the scanner struck objects, including building rooftops. You will use an ArcGIS Pro project downloaded from the solutions page that contains the 3D Basemaps solutions tools and workflows specific to local government municipal development.
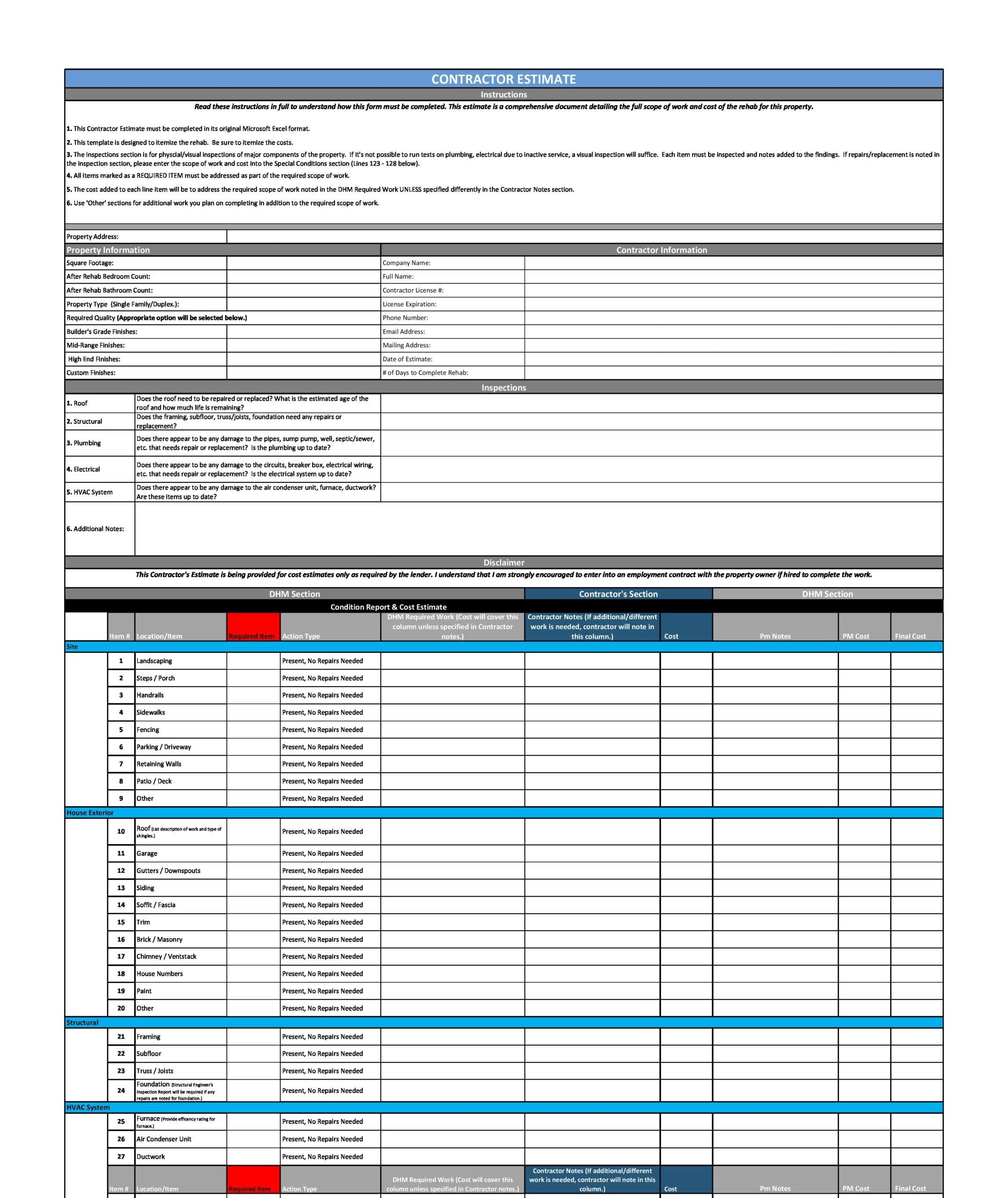
One of the best ways to determine the heights of a large number of surfaces is with lidar, a laser scanning technology that can cover large areas. To create 3D buildings with detailed roof forms and accurate heights, you must first know what those forms and heights are.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
